Continuous integration for Android with Jenkins, Docker and AWS
Recently I’ve been setting up and documenting automated build workflows for each of my projects in Jenkins. The other day it was continuous deployment of my Jekyll website, and now its continuous integration for my Android projects. My setup for Android projects utilises Docker to provision the build environments and AWS Device Farm for the integration/smoke tests.
Build Environments
Each of the Android projects have a dockerfile that defines its build environment, allowing the Jenkins pipeline to
create an environment with all the necessary SDK/API dependencies it requires for being built and tested.
The dockerfile is based on Jacek Marchwicki’s image, with a number of modifications to improve caching and SDK versioning.
FROM ubuntu:14.04
# Install Java7
RUN apt-get install -y software-properties-common && \
add-apt-repository -y ppa:webupd8team/java && \
apt-get update && \
echo oracle-java7-installer shared/accepted-oracle-license-v1-1 select true | /usr/bin/debconf-set-selections && \
apt-get install -y oracle-java7-installer
# Install Deps
RUN dpkg --add-architecture i386 && \
apt-get update && \
apt-get install -y --force-yes expect git wget libc6-i386 lib32stdc++6 lib32gcc1 lib32ncurses5 lib32z1 python curl && \
apt-get clean
# Install Android SDK
ENV ANDROID_SDK_VERSION=r24.4.1 \
ANDROID_BUILD_TOOLS_VERSION=23.0.3 \
ANDROID_API_LEVELS=android-23
RUN cd /opt && \
wget --output-document=android-sdk.tgz --quiet http://dl.google.com/android/android-sdk_${ANDROID_SDK_VERSION}-linux.tgz && \
tar xzf android-sdk.tgz && \
rm -f android-sdk.tgz && \
chown -R root.root android-sdk-linux
ENV ANDROID_HOME /opt/android-sdk-linux
ENV PATH ${PATH}:${ANDROID_HOME}/tools:${ANDROID_HOME}/platform-tools
RUN echo y | android update sdk --no-ui -a --filter tools,platform-tools,${ANDROID_API_LEVELS},build-tools-${ANDROID_BUILD_TOOLS_VERSION},extra-android-support,extra-android-m2repository,extra-google-m2repository
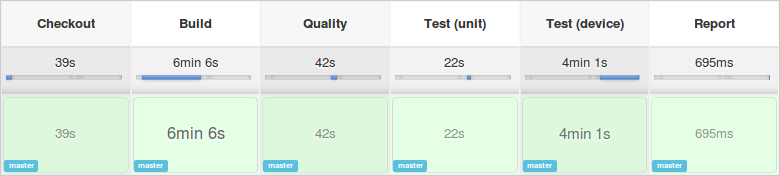
Build Pipeline
The build pipeline checks out the project’s code, and then uses the
CloudBees Docker Pipeline Plugin to
build the image from the dockerfile stored alongside the code. Once built the plugin then runs it, mounts the job’s
workspace inside of the container and executes the necessary commands to build and test the application.
After the unit tests complete (successfully I hope) then the integration tests are performed using the AWS Device Farm.
node() {
deleteDir()
stage 'Checkout'
checkout scm
stage 'Create Env'
def buildEnv = docker.build 'androidproject:latest', 'release'
buildEnv.inside {
// Create the key needed for building debug releases
sh '''mkdir -p ?/.android
keytool -genkey -v -keystore ?/.android/debug.keystore -storepass android -alias androiddebugkey -keypass android -dname "CN=Android Debug,O=Android,C=US"
'''
stage 'Build'
sh './gradlew clean assembleDebug'
archive 'app/build/outputs/**/app-debug.apk'
stage 'Quality'
sh './gradlew lint'
stash includes: '*/build/outputs/lint-results*.xml', name: 'lint-reports'
stage 'Test (unit)'
try {
sh './gradlew test'
} catch (err) {
currentBuild.result = 'UNSTABLE'
}
stash includes: '**/test-results/**/*.xml', name: 'junit-reports'
stage 'Test (device)'
sh '''./gradlew :app:assembleDebug
./gradlew :app:assembleDebugAndroidTest
'''
// Archive for downstream AWS job
archive 'app/build/outputs/**/*androidTest*.apk'
}
}
node() {
build "${env.JOB_NAME} (AWS)"
}
stage 'Report'
node() {
deleteDir()
unstash 'junit-reports'
step([$class: 'JUnitResultArchiver', testResults: '**/test-results/**/*.xml'])
unstash 'lint-reports'
step([$class: 'LintPublisher', canComputeNew: false, canRunOnFailed: true, defaultEncoding: '', healthy: '', pattern: '*/build/outputs/lint-results*.xml', unHealthy: ''])
}
Integration tests with AWS Device Farm
The integration tests carried out under the ‘Test (device)’ stage are performed using Amazon WebService’s Device Farm - which provides a far greater range of devices than I ever could. The only downside is that at the time of writing this the AWS Device Farm plugin doesn’t provide pipeline actions for Jenkins, so I’ve had to create a downstream job which uses the plugin.
Build Action
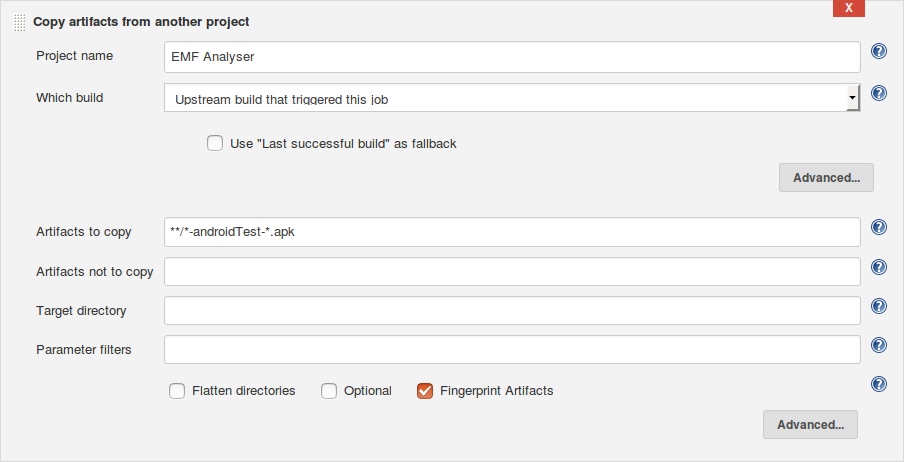
The build action of this downstream job uses the plugin Copy Artifact Plugin to copy the build artifacts archived by the upstream job using the settings:
Project name: EMF Analyser
Which build: Upstream build that triggered this job
Artifacts to copy: **/*-android-*.apk
Fingerprint Artifacts: Selected
Post-Build Action
Post build the AWS Device Farm plugin can be configured to run the integration/fuzz tests.
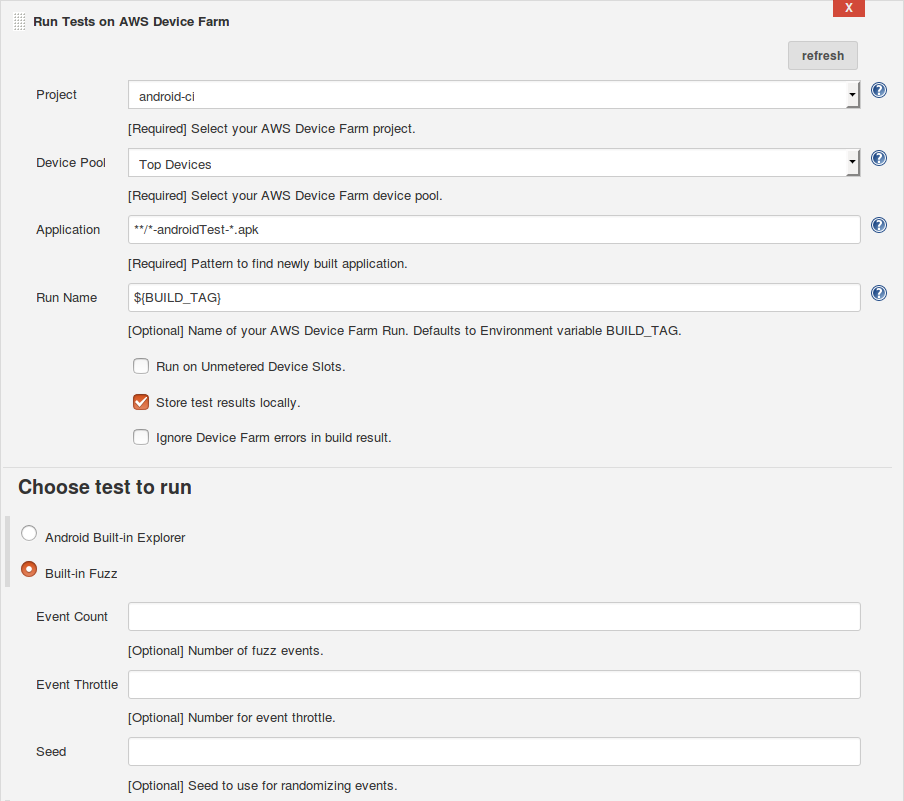
Run Tests on AWS Device Farm
Application: **/*-androidTest-*.apk